In this article, we unpacked a malicious version of the “Tous Anti Covid” application. We know the main entry point of the payload DEX is dad.calm.invest.qusalkrlkyy.

Encrypted strings
Using the decrypted payload DEX we unpacked in the previous article, we quickly notice in that class there are several encrypted strings. In this article, we’ll see how to create a JEB script to decrypt the strings.

a() is a method which first decodes Base64 and then decrypts data using a custom algorithm. This algorithm is initialized with a hard coded key. Below, I show a “de-obfuscated” version of a():
private String decrypt(String encrypted_string) {
try {
return new String(new DecryptionAlgo(this.c.key.getBytes())
.decrypt(e.createByteArray(
new String(
Base64.decode(encrypted_string, 0),
“UTF-8”))));
}...
Implementing the decryption algo in Python
I want to decrypt encrypted strings, ok? To do so, I need to understand the decryption algorithm, and automate that in a JEB script. JEB scripts are written in Python, so I’ll have to port Java code to Python.
The first thing a() does is Base64 decoding. This is easily done in Python with the base64 package and b64decode().
Then, the code converts the base64 string to a byte array and decrypts the byte array using b().
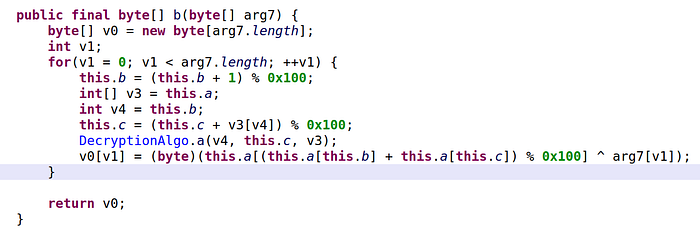
This decryption algorithm can quite easily be ported to Python:
- No need for explicit memory allocations in Python such as
new byte. We simply need to sayv0is an array[]. - The for loop is transformed to
for i in range(…). - In Python, you cannot “assign a value to an array” with
v0[v1]=.... Rather, we can “append” a value to an array. - The algorithm calls another method
a(). If you look at its code, it simply swaps the values of indicesv4andthis.cin arrayv3. That’s easy to implement in Python too.

The other part we need to take care of is the algorithm’s key. We see the code instantiates a decryption object with a hard-coded key (its value is “dcpmeyucapxy”). The object constructor prepares the key with a custom algorithm (see below).

The port of the method is not a problem, as modulo operator exist both in Java and Python.
Wrapping the algorithm into a JEB script
Once all elements of the decryption algorithm are implemented (we can test it in a standalone script), we need to wrap this up in a JEB script. JEB experts could do wonders, automatically recognize the strings, decrypt them and replace by the decrypted value (see scripts such as this one). However, I am not an expert, and I can’t spend hours on writing a script either. So, we’ll do something simpler: the JEB user is expected to select the string to decrypt, the script will automatically decrypt the string and add a comment next to it with the decrypted version. My script will not handle error cases, feel free to enhance 😄.

The JEB script (1) gets the selected string (getSelectedText or getActiveItemAsText), (2) then we send that string to the decryption algorithm we implemented. The result is the decrypted string. Finally, (3) we add that string as a comment (setComment). I largely inspired my code from this one to do that.
Source code script to decrypt strings (GitHub).
Running the script
Finally, put the Python script somewhere JEB can access it. Then, select a string to decrypt. Then, File > Scripts > Run Script. Select the script. And it should work :) The print commands go to JEB’s logger console, the decrypted string is added as comment. For next times, you can simply use F2 to run the same script.
Very handy! Have a look at the video to see it in action.
— cryptax
